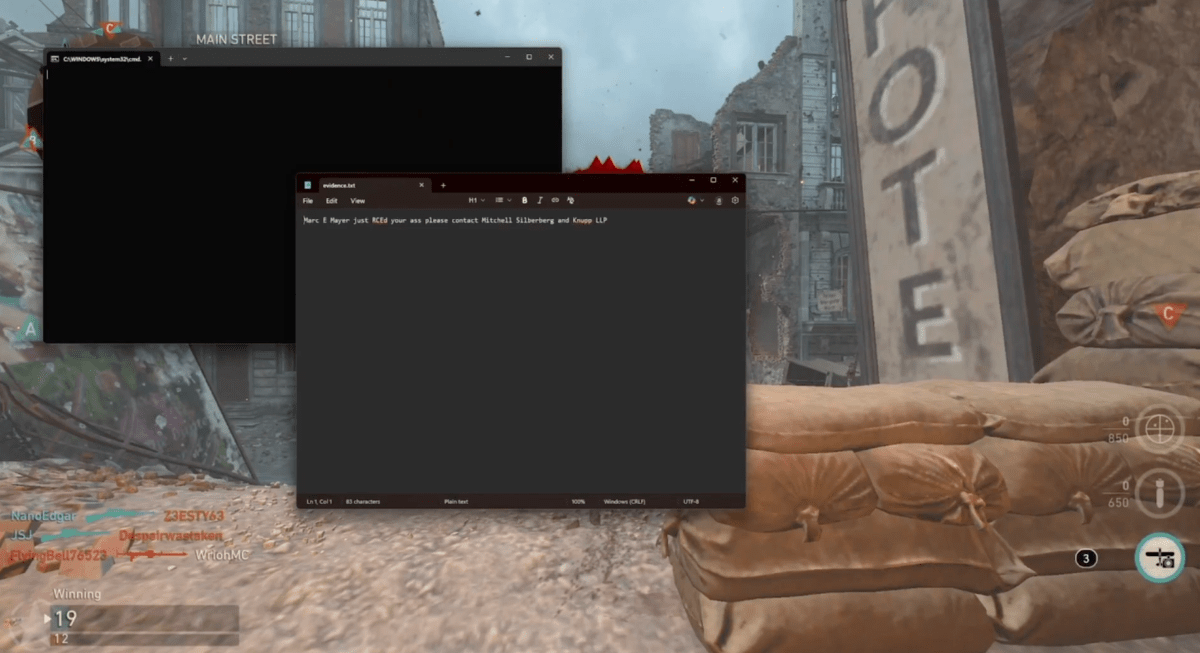
In a shocking turn of events, the beloved first-person shooter Call of Duty: WWII has been pulled from PC platforms due to alarming reports of a Remote Code Execution (RCE) exploit. This exploit has allowed hackers to commandeer players’ computers during live matches, sparking widespread chaos and concern within the gaming community.
The vulnerability, which primarily affects the PC version available through Microsoft’s Game Pass, has been exploited to execute arbitrary code on users’ machines. Gamers have reported a range of disruptive activities, from unexpected system shutdowns to the sudden appearance of inappropriate desktop wallpapers.
The Rise and Fall of Call of Duty: WWII on PC
Call of Duty: WWII was recently introduced to Game Pass, expanding its reach to a broader audience. However, this move inadvertently exposed more players to the exploit. The game’s reliance on peer-to-peer networking, a legacy architecture that allows one player’s machine to act as a server, has been identified as the root cause of this security lapse. This setup, while cost-effective, leaves systems vulnerable to malicious attacks.
Industry Response and Security Concerns
Activision, the game’s publisher, has temporarily taken the game offline and is investigating the issues. Despite the offline status, the exploit’s impact has already been felt, with many players expressing frustration and concern over the breach. Security experts emphasize the need for robust anti-cheat systems and regular updates to prevent such vulnerabilities.
The concern in this particular case is that this means an attacker is capable of deploying information stealer malware, a RAT (remote administration tool), or ransomware. Thankfully, it appears this attacker is primarily interested in memeing and messing with people.
— VX-Underground
The Future of Game Security
This incident highlights a critical issue within the gaming industry: the security of legacy games. As older titles migrate to modern platforms like Game Pass, they bring with them vulnerabilities that pose significant risks to players. The industry is now under pressure to ensure that such games receive security updates and patches to protect users from emerging threats.
Conclusion
The Call of Duty: WWII incident serves as a wake-up call for both developers and players. As gaming continues to evolve with new technological advances, ensuring the security of older titles must remain a priority. For players, vigilance is crucial—staying informed about security updates and potential threats can safeguard personal data and enhance the gaming experience. As the industry grapples with these challenges, one thing is clear: proactive security measures are not just optional but essential.